When it comes to job applications, the terms “resume” and “CV” (Curriculum Vitae) often create confusion among job seekers. While both documents serve as professional summaries of qualifications, skills, and experiences, they are used differently depending on the region, industry, and specific job requirements.
Understanding the differences and knowing when to use each can significantly improve your chances of landing your desired job. This comprehensive guide on Resume vs CV will help you decide whether a resume or CV is the right choice for your application.
Table of Contents
Understanding Resume vs CV by Definition
What Is a Resume?
A resume is a concise, tailored document that highlights your professional achievements, skills, and relevant work experience. Its purpose is to provide a snapshot of your qualifications to catch the employer’s attention quickly.
Key Characteristics of a Resume
- Length: Typically 1-2 pages.
- Content: Focuses on relevant work experience, skills, and achievements tailored to the job you’re applying for.
- Structure: Includes sections like a professional summary, work experience, education, and skills.
- Customization: Tailored for each job application by incorporating keywords and aligning with the job description.
Resumes are widely used in countries such as the United States, Canada, and Australia, where brevity and customization are highly valued in the hiring process.
What Is a CV (Curriculum Vitae)?
A CV, derived from the Latin phrase “Course of Life,” is a more detailed document that provides an in-depth overview of your academic and professional history. It is commonly used in academic, research, and medical fields.
Key Characteristics of a CV
- Length: Can range from 2 to 10+ pages, depending on the individual’s career history.
- Content: Includes detailed information on education, research, publications, presentations, awards, and professional affiliations.
- Structure: Chronological and comprehensive, with no emphasis on tailoring for a specific job.
- Usage: Often required in Europe, Asia, and academic or research-based industries worldwide.
Differences Between Resume and CV
A resume and a CV (Curriculum Vitae) differ significantly in purpose, structure, and usage. A resume is a concise, one- to two-page document that highlights your skills, experiences, and achievements tailored to a specific job role. It’s widely used in regions like the United States and Canada for applying to corporate or non-academic positions.
In contrast, a CV is a more comprehensive and detailed document that provides an in-depth overview of your professional journey, including academic accomplishments, publications, and research. CVs are commonly used in Europe, Asia, and academic or research fields worldwide. While resumes emphasize brevity and customization, CVs focus on providing a complete career history, making each document suitable for different purposes and audiences.
| Aspect | Resume | CV |
|---|---|---|
| Length | 1-2 pages | 2+ pages, depending on experience |
| Purpose | Tailored for specific jobs | Comprehensive history of academic/professional life |
| Focus | Skills, achievements, relevant experience | Academic achievements, research, publications |
| Customization | Tailored for each job application | Standardized; not tailored |
| Structure | Flexible, focuses on most recent/relevant info | Fixed, chronological order |
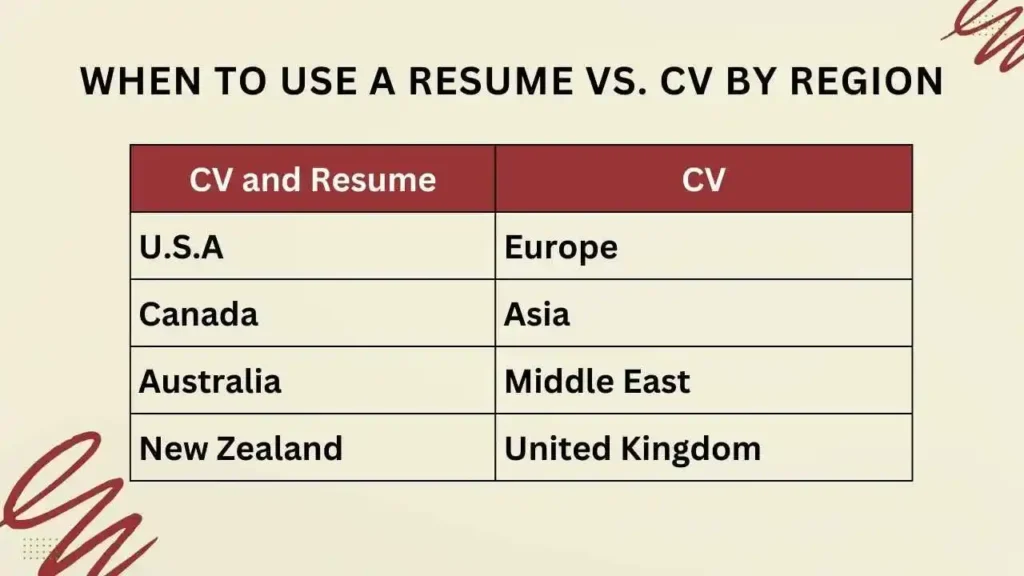
| Geographical Use | USA, Canada, Australia | Europe, Asia, Middle East, academic settings |
When to Use a Resume vs. CV by Region
United States and Canada
- Use a Resume: Most industries, especially corporate, technical, and creative fields.
- Use a CV: Academic, research, and medical positions.
Europe
- Use a CV: The term “CV” is commonly used in Europe, and it typically refers to a detailed document similar to what Americans call a resume. However, it should still include more information, such as references and detailed education history.
EURES: Finding a Job in Europe – A Guide for Jobseekers provides essential tips, resources, and insights to help you navigate the European job market and secure your ideal position.
Australia and New Zealand
- Use a Resume: Preferred for job applications, focusing on brevity and relevance.
- Use a CV: Rarely used unless specified for academic or research roles.
Asia and Middle East
- Use a CV: Employers in these regions often request a detailed CV, including personal information like nationality, date of birth, and even a photo, depending on cultural norms.
United Kingdom
- Use a CV: In the UK, a CV is similar to a resume in the US but slightly more detailed, typically spanning two pages.
When to Use a Resume vs. CV by Industry
Resume Preferred
- Corporate/Business: Resumes work well for industries like finance, marketing, and IT, where concise and tailored information is valued.
- Creative Fields: Graphic design, content writing, and advertising roles require resumes that highlight creativity and relevant achievements.
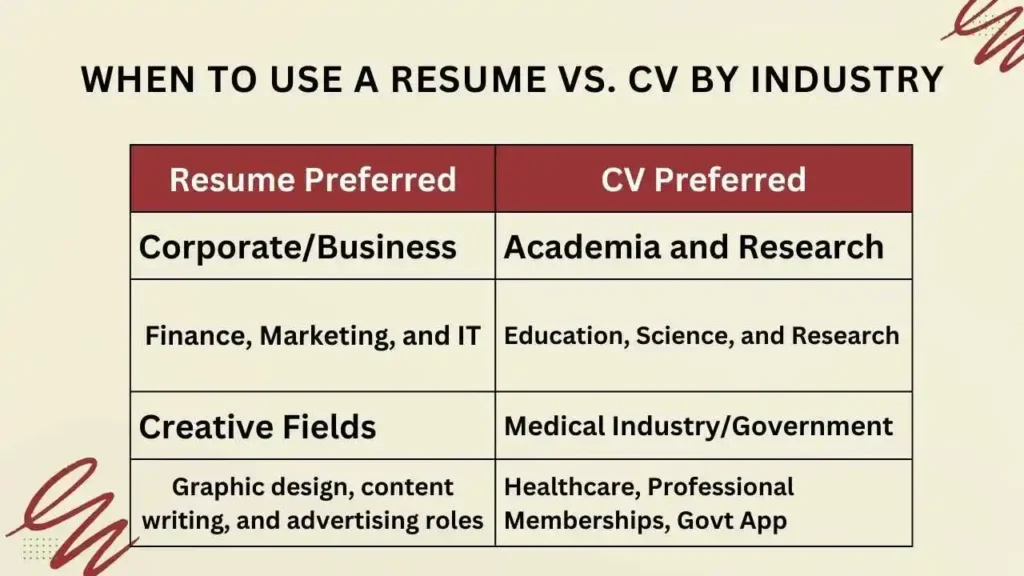
CV Preferred
- Academia and Research: Fields such as education, science, and research require a detailed CV, including publications, research papers, and conferences attended.
- Medical Industry: Healthcare professionals often use a CV to highlight their certifications, residencies, and professional memberships.
- Government Roles: In some regions, government applications may request a CV to include detailed career history.
How to Decide Between a Resume and CV
- Review the Job Description: Some postings explicitly state whether a resume or CV is required.
- Consider the Region: Be mindful of the hiring practices in the region where you’re applying.
- Evaluate the Industry: Understand the expectations of your industry, especially for specialized fields like academia or research.
- Contact the Employer: If you’re unsure, reach out to the hiring manager or HR department for clarification.
Tips for Creating an Effective Resume or CV
For Resumes
- Use bullet points to highlight achievements concisely.
- Tailor your resume for each job by using keywords from the job description.
- Focus on measurable results (e.g., “Increased sales by 20%”).
- Keep formatting clean and professional.
For CVs
- Include all relevant academic achievements, research, and certifications.
- Maintain a clear structure with headings like “Education,” “Research,” and “Publications.”
- Avoid irrelevant details; focus on academic and professional accomplishments.
- Ensure the document is well-organized and easy to navigate, even if lengthy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Using the Wrong Document: Sending a resume when a CV is required (or vice versa) can harm your chances.
- Lack of Tailoring: Failing to customize your resume for the job application can make it less appealing.
- Overloading a Resume: Resumes should be concise; avoid including unnecessary details.
- Underrepresenting in a CV: Ensure your CV is detailed and complete, especially in academic settings.
Are you looking for the professional cover letter support and Ideas? Then, read our blog post on “10 Different Types of Cover Letters with Sample Examples & Tips: Which One Do You Need?”
FAQs on What is the difference between a resume and a CV
Can I use a resume instead of a CV for academic roles?
While resumes are acceptable in some cases, academic roles usually require a detailed CV that includes research and publications.
How long should a CV be?
A CV can be as long as necessary to include all relevant information, typically 2-10 pages depending on experience.
Is a photo required in a resume or CV?
It depends on the region. Photos are generally not required in the US and Canada but are commonly included in Europe and Asia.
Can I use the same document for every job application?
No, resumes should be tailored for each job. However, CVs are typically standardized and updated as needed.
How often should I update my resume or CV?
You should update your documents regularly, especially after completing significant projects, earning certifications, or starting new roles.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between a resume and a CV can significantly enhance your job application process. A resume is the best choice for most corporate and creative roles, especially in regions like the US and Canada, where brevity and customization are valued. Conversely, a CV is more appropriate for academic, medical, or research-based positions and is commonly used in Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
By tailoring your approach to the job, region, and industry, you can ensure that your application stands out and demonstrates your professionalism. Whether you’re crafting a concise, impactful resume or a detailed, comprehensive CV, the key is to present yourself in the best possible light for the role you’re pursuing.
“Need help crafting a professional resume or CV? Explore our templates and expert services today!”







Good effort. Enough knowledge for beginners
Thank you.
very helpful published by Israr.
Thank you
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you. Yes. You can ask please.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
It is my pleasure that you are getting insight and having relaxation after reading our posts. Hopefully, your career will develop now. Stay tune for more updates and subscribe to our newsletter.
Regards
I couldn’t stop scrolling and reading, your content is truly one-of-a-kind. Thank you for all the time and effort you put into creating such amazing content.
I really appreciate you for the words and happy that you really enjoyed reading our blogs.
My pleasure
I am happy that it work for you and you have gain the knowledge. Stay tune for more updates.
I have been struggling with this issue for a while and your post has provided me with much-needed guidance and clarity Thank you so much
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Great!
Thank you. Stay connected for more updates.
Your blog always leaves me feeling uplifted and inspired Thank you for consistently delivering high-quality content
Thank you